What is the pancreas?
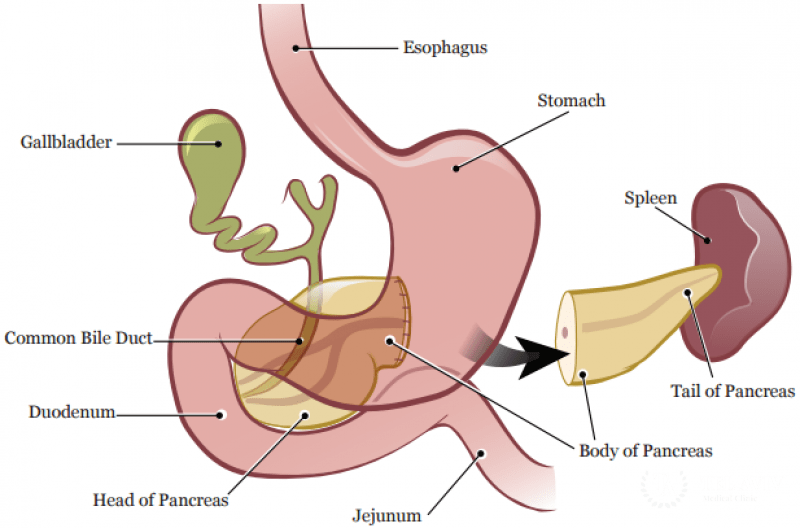
The pancreas is an organ located in the abdomen. It plays an essential role in converting the food we eat into fuel for the body’s cells. The pancreas has two main functions: an exocrine function that helps in digestion and an endocrine function that regulates blood sugar.
What is pancreatic cancer?
Pancreatic cancer occurs when changes (mutations) in the pancreas cells lead them to multiply out of control. A mass of tissue can result. Sometimes, this mass is benign (not cancerous). In pancreatic cancer, however, the mass is malignant (cancerous). Dr. Manoj Dongare provides the best Pancreatic Cancer Treatment in Pune. He is the best cancer specialist in Pune.
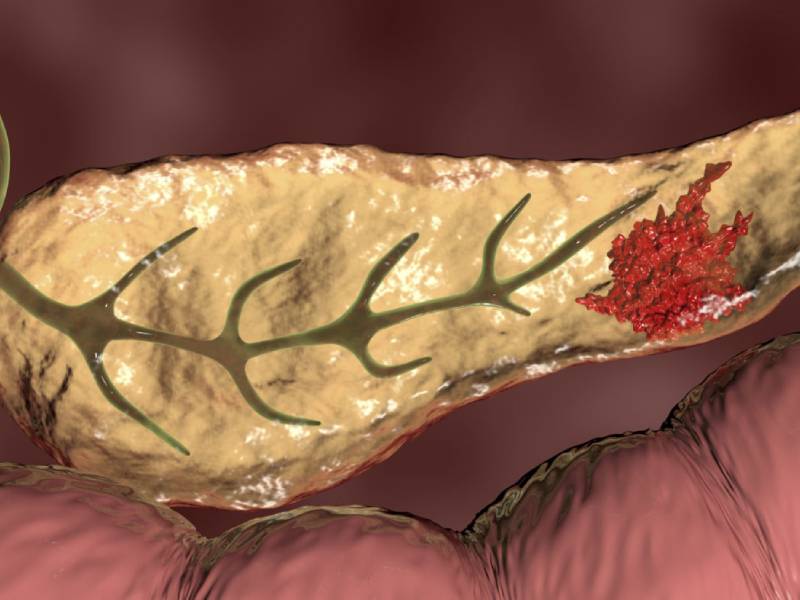
What are the symptoms of pancreatic cancer?
Most people don’t experience early signs of pancreatic cancer. As the disease progresses, however, people may notice:
- Upper abdominal pain that may spread to the back.
- Yellowing of the skin and the whites of the eyes (jaundice).
- Tiredness.
- Loss of appetite.
- Light-colored poop.
- Dark-colored pee.
- Weight loss.
- Blood clots in the body.
- Itchy skin.
- New or worsening diabetes.
- Nausea and vomiting
If you notice any of the symptoms, you must visit an HPB Surgeon doctor in Pune at the earliest. The fastest assessment and subsequent treatment will help you combat this medical condition and live a better life.
Pancreatic cancer risk factors:
Anything that increases your chance of developing pancreatic cancer is a risk factor. Some risk factors can be changed, while others cannot. Risk factors that can be changed include:
- Smoking and tobacco use: People who smoke are about twice as likely to develop pancreatic cancer.
- Obesity: Being very overweight (having an elevated body mass index, or BMI) increases your chance of developing pancreatic cancer by 20%.
- Having diabetes, especially type 2 diabetes, is linked to obesity.
- Chronic pancreatitis: Long-term inflammation of the pancreas is linked with increased pancreatic cancer risk, especially in smokers.
How Pancreatic Cancer is diagnosed?
Pancreatic cancer symptoms usually do not appear in the early stages. Several diagnostic tests are usually required to find and stage (determine the extent of) pancreatic cancer. Following methods such as blood tests, diagnostic imaging tests, and biopsy are used for detecting pancreatic cancer.
A) Blood Test: There are multiple blood tests that can be helpful for diagnosing pancreatic cancer such as
- Liver function test: Measures liver enzymes and levels of bilirubin (pancreatic cancer causes elevated bilirubin in the blood)
- CA19-9: Measures a type of protein in the blood that is often associated with pancreatic cancer (this protein can be present in non-cancerous conditions as well)
- Carcinogenic Antigen (CEA): Measures a type of protein in the blood (different from CA19-9) that is often associated with pancreatic cancer (this protein can be present in non-cancerous conditions as well)
B) Imaging Tests: Diagnostic imaging tests can see the location of a tumor and indicate whether cancer cells have spread, or metastasized, to other parts of your body. Which includes
- CT scan: A painless, outpatient procedure that uses a series of X-rays taken from different angles to provide an image of the pancreas.
- MRI scan: A painless, outpatient procedure that uses magnets, rather than x-rays, to provide an image of the pancreas.
- Endoscopic ultrasound: A special endoscope with an ultrasound probe is inserted into the mouth and directed to the first part of the small intestine to show the pancreas on a video screen.
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP): A special endoscope is inserted through the mouth and directed to the first part of the small intestine. A smaller tube is then inserted through the endoscope into the bile ducts.
C) Biopsy: Although there are multiple diagnostic approaches to detecting pancreatic cancer, the most accurate way is by taking a sample of tissue (biopsy), which can be evaluated under a microscope. A biopsy can be performed during EUS or ERCP, or by a radiologist inserting a needle to withdraw tissue while under anesthesia.
Prevention of Pancreatic Cancer:
No specific measure can prevent pancreatic cancer, but some lifestyle choices can help reduce the risk.
These include:
- Don’t smoke. If you do smoke or use tobacco in any form, try to quit.
- Try to reach and maintain a normal weight by eating healthy and exercising.
- Drink alcohol in moderation, or quit drinking altogether.
- Try to avoid getting diabetes. If you have it, control your blood sugar levels.
- Use safety equipment if your work exposes you to toxins.
Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer:
Treatment options for pancreatic cancer depend on the type and stage of cancer. Medical research is ongoing to determine the best methods for relieving pain and eliminating cancer..
A) Operable pancreatic tumor:
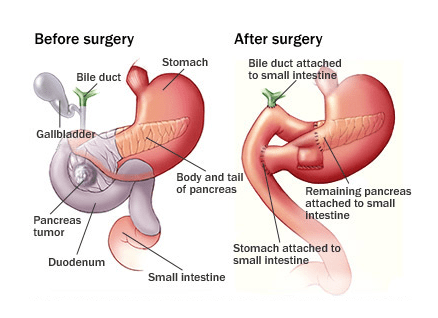
If a tumor of the pancreas is localized and blood vessels are not impacted by the tumor, surgery is often recommended to remove the tumor. In many cases after surgery, the physician will recommend additional therapy to prevent cancer from growing back, such as chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or both. There are several different types of surgeries used to remove a localized pancreatic tumor. As technology has advanced, options for surgical intervention have advanced, but the type of surgery recommended depends on the stage of cancer and the location of the tumor.
- Whipple Procedure: It is often used to remove tumors in the head of the pancreas
- Distal Pancreatectomy: It is often used to remove tumors in the tail of the pancreas
- Total Pancreatectomy: It is removal of the entire pancreas, and often removal of gallbladder, spleen, and other areas as deemed necessary by the surgeon.
- Central Pancreatectomy: It is removal of the middle of the pancreas
B) Borderline operable tumor:
If the tumor is partially adherent to the portal vein or close to the neighboring arteries usually few cycles of chemo or Chemo followed by radiation is given. CT scan or MR is repeated in a few weeks and the response assessed. If there is a good response or stable disease, The patient is taken for Surgery. However, if the disease progresses during this period patient is referred for palliative treatment.
C) Locally Advanced Tumor:
If a tumor is stuck to blood vessels which prevents its resection, surgery is not usually recommended because of potential complications. For many locally advanced tumors, physicians will recommend chemotherapy and radiation therapy as definitive treatment.
D) Metastatic tumors:
Palliative chemo, stenting for jaundice, duodenal Bypass for obstruction are the options. Palliative treatment options include stenting of the obstructed biliary tree (to relieve jaundice), surgical biliary bypass (especially in younger patients), and complex pain-relief options. In addition, enzyme supplements may be useful because the main pancreatic duct is usually blocked. Chemotherapy is an option and has been shown to increase the chance of survival, especially over longer periods of time. Curative treatment options include partial or total removal of the pancreas to prevent metastasis. Postoperative morbidity is high (30%–40%), and patients generally require intensive care for at least 24 hours after surgery
What is the cost of Pancreatic Cancer Treatment in Pune?
The cost of Pancreatic cancer treatment in Pune may depend upon the following factor
- Type of treatment recommended by Liver Cancer Surgeon
- Duration of hospitalization
- Room category
- Additional medical tests, if required
- Expense for medications
- Government Scheme (If Applicable)
Book an Appointment:
Dr. Manoj Dongare at Dr. D. Y. Patil Hospital and Research Center provides one of the best treatments for various Liver diseases in Pimpri Chinchwad Pune. For more information about our comprehensive treatment options, or to request an appointment with the best HPB and Liver Transplant surgeon in Pune call 09881379573 or Click on Book Appointment for online booking with your near hospital.
